-
摘要: 针对膏体充填技术中添加絮凝剂对尾砂浓密后浓度提高有限,且屈服应力增大,流动性降低等问题,研究了絮凝剂−浓密增效剂共同作用,进一步提高全尾砂膏体充填料浆浓度,降低料浆屈服应力,并从微观角度进行机理分析. 结果表明:通过沉降与流变试验发现,最佳添加工艺为加入絮凝剂沉降完毕后再加入浓密增效剂,固相质量分数可提高8.57%~10.13%,同时屈服应力降低6.68~12.85 Pa;多组分浓密增效剂不仅能降低单耗与成本,还可以提高膏体充填材料的抗压强度;灰砂质量比1∶12并添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料28 d抗压强度为2.5 MPa,与灰砂质量比1∶6未添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料强度相差小于20%;通过总有机碳(TOC)吸附试验与Zeta电位试验发现,浓密增效剂具有吸附与分散的作用,会打开絮凝结构,释放絮团间水,从而提高尾砂浓度,并改善尾砂颗粒的流动性.Abstract: The mine tailings generated from metallic ore not only occupies a large area of surface resources but also easily causes mud-rock flow and tailings dam failure. Moreover, the existence of a large number of underground voids threatens the safety of underground mining operations and can induce mines earthquake and surface subsidence. The paste filling technology involves thickening the mine tailings into paste and placing the paste in underground voids. The technology has been widely accepted and applied around the world for its advantages in safety, environmental protection, economy, and high efficiency. The dewatering of mine tailings is a prerequisite for the paste filling process. In the paste backfill, after tailings thickening, the concentration increase is limited, the yield stress is increased, and fluidity is reduced with flocculant dosage. The flocculant dosage and thickening synergist work together to further increase unclassified tailings paste concentration and reduce slurry yield stress. The mechanism of the thickening synergist was researched from a microscopic point of view. The results show that the best addition method is to add thickening synergist after tailings settlement with flocculant dosage by settlement and rheological test. The solid mass fraction can be increased by 8.57%‒10.13%, and the yield stress can be reduced by 6.68‒12.85 Pa. The multi-component thickening synergist can not only reduce unit consumption and cost but also improve the compressive strength of the paste backfill material. The compressive strength of paste backfill material with thickening synergist and cement-tailings mass ratio of 1∶12 is 2.5 MPa at the age of 28 d. The difference is less than 20% compared with the compressive strength of the material with cement-tailings mass ratio of 1∶6 and without thickening synergist. By total organic carbon adsorption test and Zeta potential test, the synergist is found to have functions of adsorption and dispersion. It can destroy the flocculation structure and release the contained water, thereby increasing the tailings concentration and improving the fluidity of tailings particles.
-
Keywords:
- paste backfill /
- slurry thickening /
- thickening synergist /
- mechanism /
- adsorption and dispersion
-
金属矿开采过程中伴随着大量的尾矿砂,不仅占用地表资源,而且容易诱发尾矿库溃坝事故。同时,大量采空区的存在,既威胁井下作业的安全,又易诱发矿震和地表塌陷[1]。随着我国经济的发展和对环境的要求,资源开发必须与环境协调,绿色开采技术必将受到充分重视[2],而膏体充填技术在安全、环保、经济、高效等方面具有综合优势[3-6]。
浓密脱水是膏体充填工艺的前提。现场多采用深锥浓密机[7-9]对尾砂进行脱水浓密,添加絮凝剂可以提高尾砂的沉降速度。吴爱祥等[10]研究了多因素耦合作用下尾砂絮凝沉降规律,焦华喆等[11]、李辉等[12]研究相同絮凝剂单耗下,给料浓度与沉降速度的相关性,王勇等[13-14]研究絮凝剂稀释倍数与添加时间对尾砂沉降的影响,杨柳华等[15]研究了絮凝剂种类与单耗对尾砂料浆流变特性的影响。总体而言,目前国内外对全尾砂膏体浓密添加剂的研究方面只停留在絮凝剂,絮凝剂的添加有助于提高尾砂沉降速度,但同时也会增加液体渗流阻力,增加浆体屈服应力。并且由于絮凝剂与尾砂颗粒形成紧密的絮团结构,现有方法无法使絮团内部的水全部排出,限制了底流浓度的进一步增高。
针对尾砂脱水浓密工艺存在底流浓度提高程度受限、流动性差等弊端,本文设想采取絮凝剂−浓密增效剂共同作用的方法,进一步提高全尾砂膏体充填料浆浓度,并能达到管道输送的流动性。本文采用某矿全尾砂制备低浓度尾砂料浆,进行尾砂沉降与流变试验,研究浓密增效剂对尾砂料浆沉降后浓度、流变性能以及不同灰砂比的硬化体抗压强度的影响;通过总有机碳(TOC)吸附试验与Zeta电位试验探讨浓密增效剂的作用机理。
1. 原材料与试验方法
1.1 试验原材料
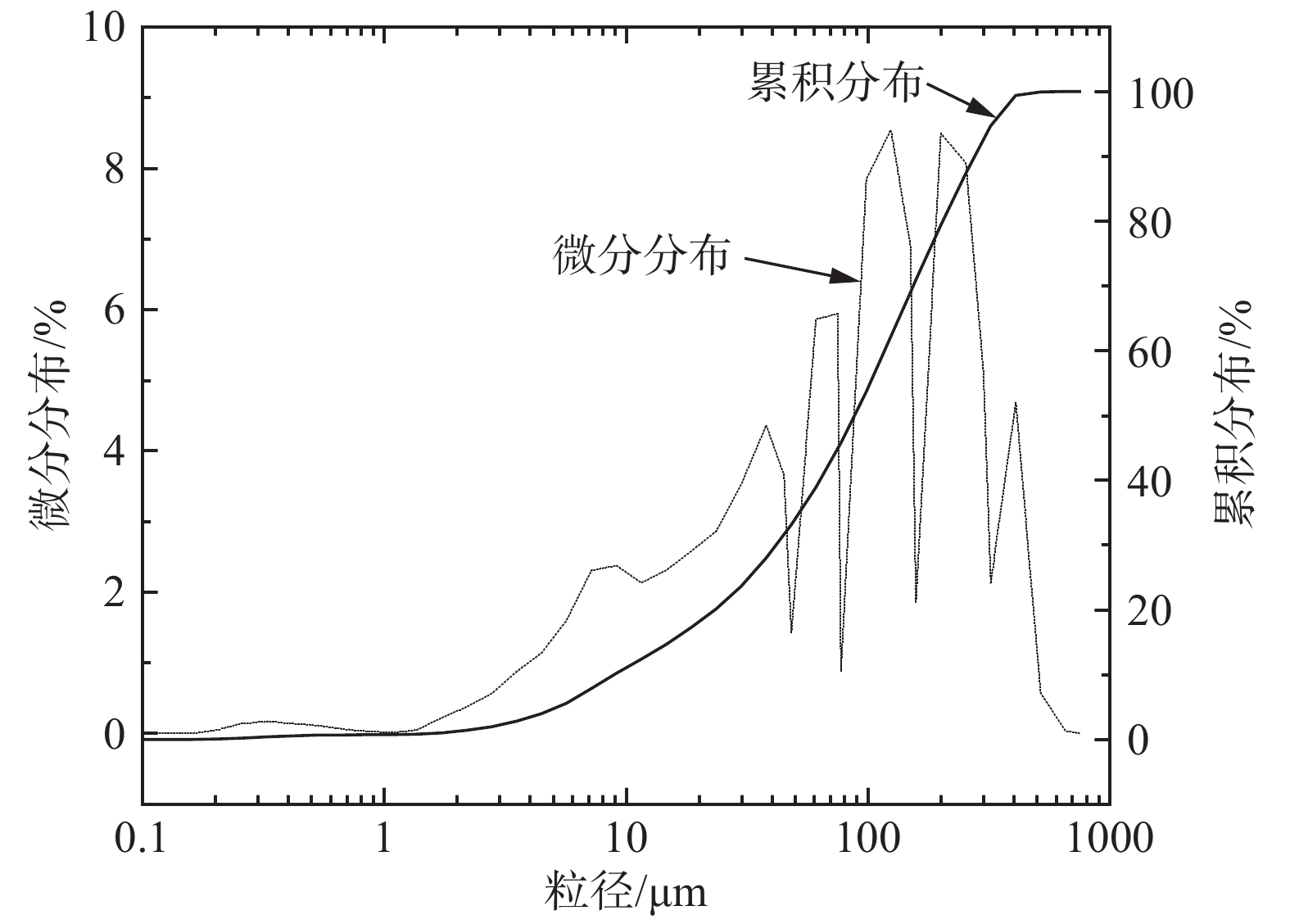
尾砂:采用某矿全尾砂,其粒径分布如图1所示,−75 μm的颗粒占比为44.89%;其化学成分见表1,氧化硅与氧化铝的含量较多,其中烧失量为1.16%。
表 1 尾砂的化学成分(质量分数)Table 1. Chemical composition of tailings% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 K2O MgO CaO MnO Na2O TiO2 SO3 P2O5 65.83 16.89 2.30 7.46 0.31 3.46 0.08 1.53 0.29 0.60 0.09 絮凝剂:采用德国巴斯夫股份公司(BASF)生产的絮凝剂,溶解为溶质质量分数为1%的溶液。
浓密增效剂:单组分浓密增效剂由一种物质组成;多组分浓密增效剂由3种或4种物质组成,将几种物质的粉体按照一定比例混合均匀后,溶解为溶质质量分数为10%的溶液。多组分浓密增效剂包含络合组分、胺类组分与水溶性高分子聚合物组分。
水:实验室自来水,温度为20±2 ℃。
1.2 试验方法
沉降试验:将尾砂制作成低浓度料浆,倒入1000 mL的量筒中,加入外加剂并匀速搅拌,记录不同时刻固液分离面高度与沉降速度变化。其中外加剂的添加方式根据外加剂的种类与添加顺序不同分为3种:第一种为单掺絮凝剂,将絮凝剂加入量筒中,与尾砂料浆共同匀速搅拌;第二种为加入絮凝剂沉降完毕后加入浓密增效剂,量筒中的尾砂料浆在絮凝剂的作用下沉降完毕后,使用吸管将上清液去除,再加入浓密增效剂,并与量筒中的尾砂料浆共同匀速搅拌;第三种为絮凝剂与浓密增效剂同时加入,即先将絮凝剂加入量筒中,紧接着加入浓密增效剂,两种外加剂与尾砂料浆共同匀速搅拌。
流变性能:采用Brookfield的RST型流变仪,将四叶桨式转子浸入料浆中,以变化剪切速率旋转,转子规格为V40-20型桨式转子。
抗压强度:采用WDW-50型微机控制电子万能试验机测试试块不同龄期的抗压强度值,试块尺寸为70.7 mm的立方体。
碳吸附试验:采用美国IONICS公司生产的TOC分析仪。按比例配制浆体并加入添加剂,搅拌3 min,再静置5 min,浆体达到吸附平衡后,用离心机(转速为4000 r·min−1)分离10 min,取上层清液再次离心分离,加入去离子水稀释,并测定滤液中有机碳的含量;配制相同比例的添加剂溶液做对比组,搅拌3 min,再静置5 min,加入去离子水稀释,并测定溶液中有机碳的含量。
Zeta电位试验:采用上海中晨数字技术设备有限公司生产的JS94H型微电泳仪。按比例配制浆体并加入添加剂,搅拌均匀,取少许净浆用去离子水稀释500倍,在磁力搅拌器中搅拌5 min,然后测试Zeta电位。
2. 结果分析
2.1 单组分浓密增效剂对全尾砂料浆浓密性能的影响
将尾砂制作成低浓度(固相质量分数为25%)料浆,倒入1000 mL的量筒中,试验分为3组。(1)单掺絮凝剂,絮凝剂单耗为20 g·t−1,记为1#;(2)加入絮凝剂沉降完毕后加入浓密增效剂,浓密增效剂单耗为1400 g·t−1,记为2#;(3) 絮凝剂与浓密增效剂同时加入,絮凝剂与浓密增效剂的掺量不变,记为3#。处理1 t尾砂,浓密增效剂的成本为28元.
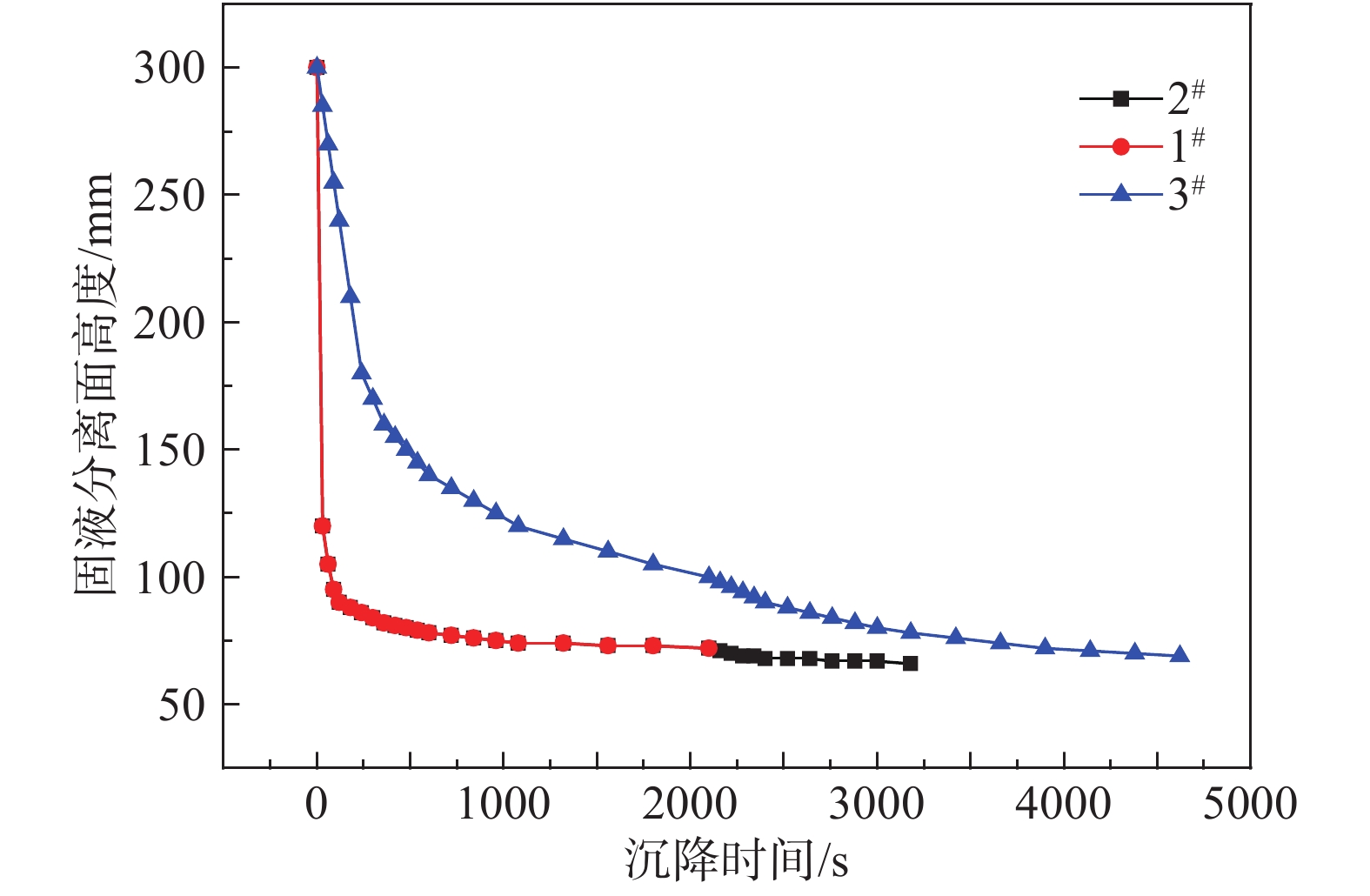
尾砂沉降过程中量筒出现3个区域,自上而下分别为澄清区、沉降区和沉淀区,澄清区越来越大,沉淀区越来越小,稳定后沉降区消失。尾砂料浆从1000 mL刻度,即对应量筒高度为300 mm处,降到最终刻度过程中固液分离面高度随时间变化的曲线如图2所示。单独添加絮凝剂后,前两组尾砂从300降到90 mm所用时间均为2 min,沉降较快,90 mm高度之后沉降较慢,第2组的浓密增效剂在72 mm高度时加入。由图2可以看出,加入浓密增效剂后,固液分离面高度继续下降,下降幅度为6 mm。第3组的絮凝剂与浓密增效剂同时加入,则尾砂沉降较慢,沉降时间是第二组的1.5倍。
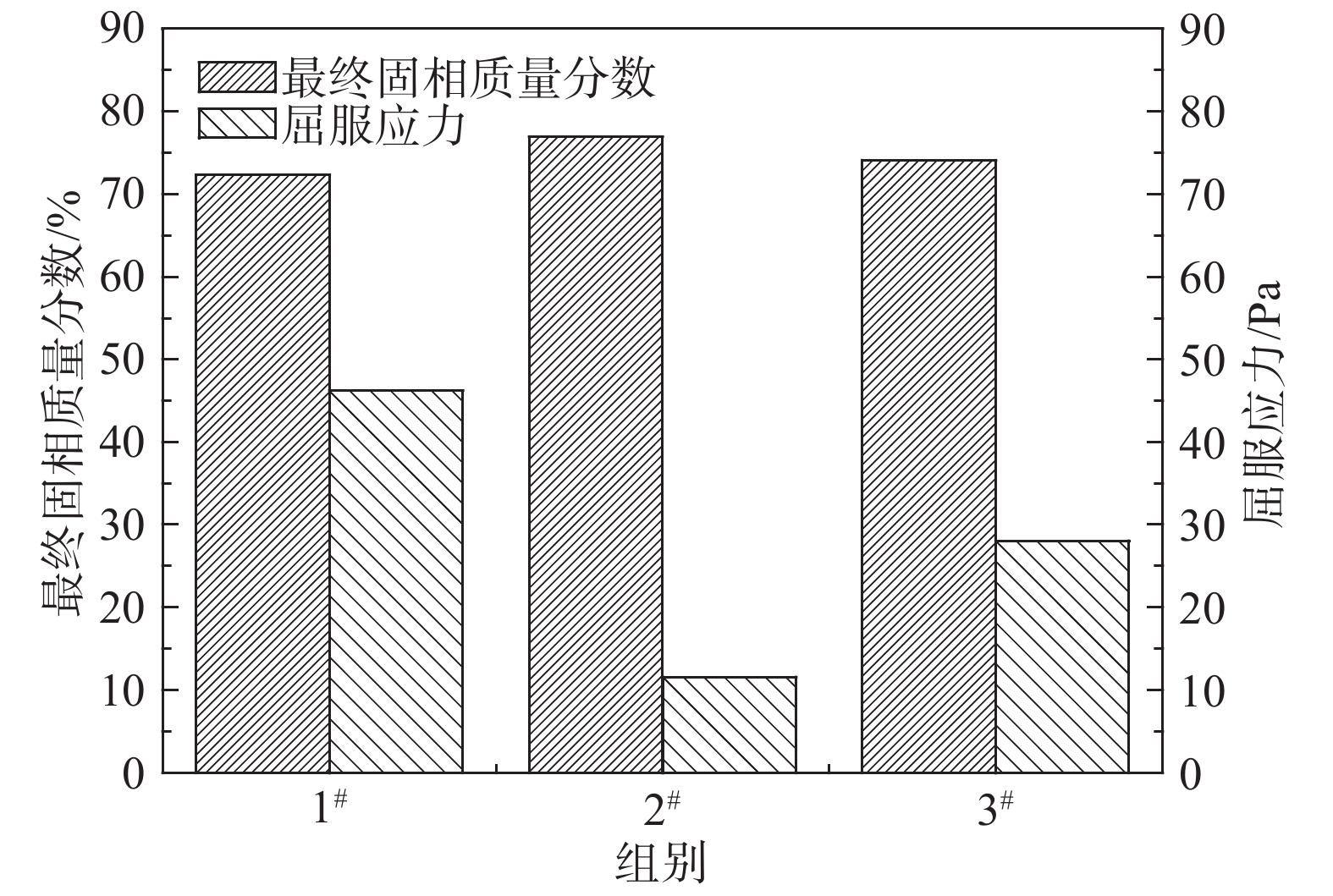
通过计算得到3组试验尾砂料浆沉降的最终固相质量分数分别为72.29%、76.92%、74.07%,如图3所示。添加浓密增效剂后浓度分别增加了4.63%与1.78%,且水柱澄清,说明浓密增效剂发挥了作用,且加入絮凝剂沉降完毕后再加入浓密增效剂的浓度增加较多且沉降时间增加较少,效果较好,因此可以确定其为最佳添加工艺。
通过流变仪测试尾砂料浆浓密后的流变性能,得到屈服应力与塑性黏度两个流变参数,屈服应力分别为46.21、11.58和28.05 Pa,如图3所示。塑性黏度分别为0.23、0.90和0.44 Pa·s。其中第2种添加方式,添加浓密增效剂后尾砂料浆屈服应力降低了34.63 Pa,塑性黏度变化较小。说明浓密增效剂可以改善尾砂浓密后的流变性能,从而有利于管道输送。
2.2 多组分浓密增效剂对全尾砂料浆浓密性能的影响
单组分浓密增效剂的单耗与成本较高,为进一步降低浓密增效剂的单耗与成本,笔者尝试了多种不同种类、不同配比和不同掺量的添加剂,从中选择效果最佳的多组分浓密增效剂。将尾砂制作成低浓度(固相质量分数25%)料浆,倒入1000 mL的量筒中,进行多组试验,均为加入絮凝剂沉降完毕后加入浓密增效剂,絮凝剂掺量不变,浓密增效剂单耗为500~1100 g·t−1。处理1 t尾砂,浓密增效剂的成本为6.2~16元。
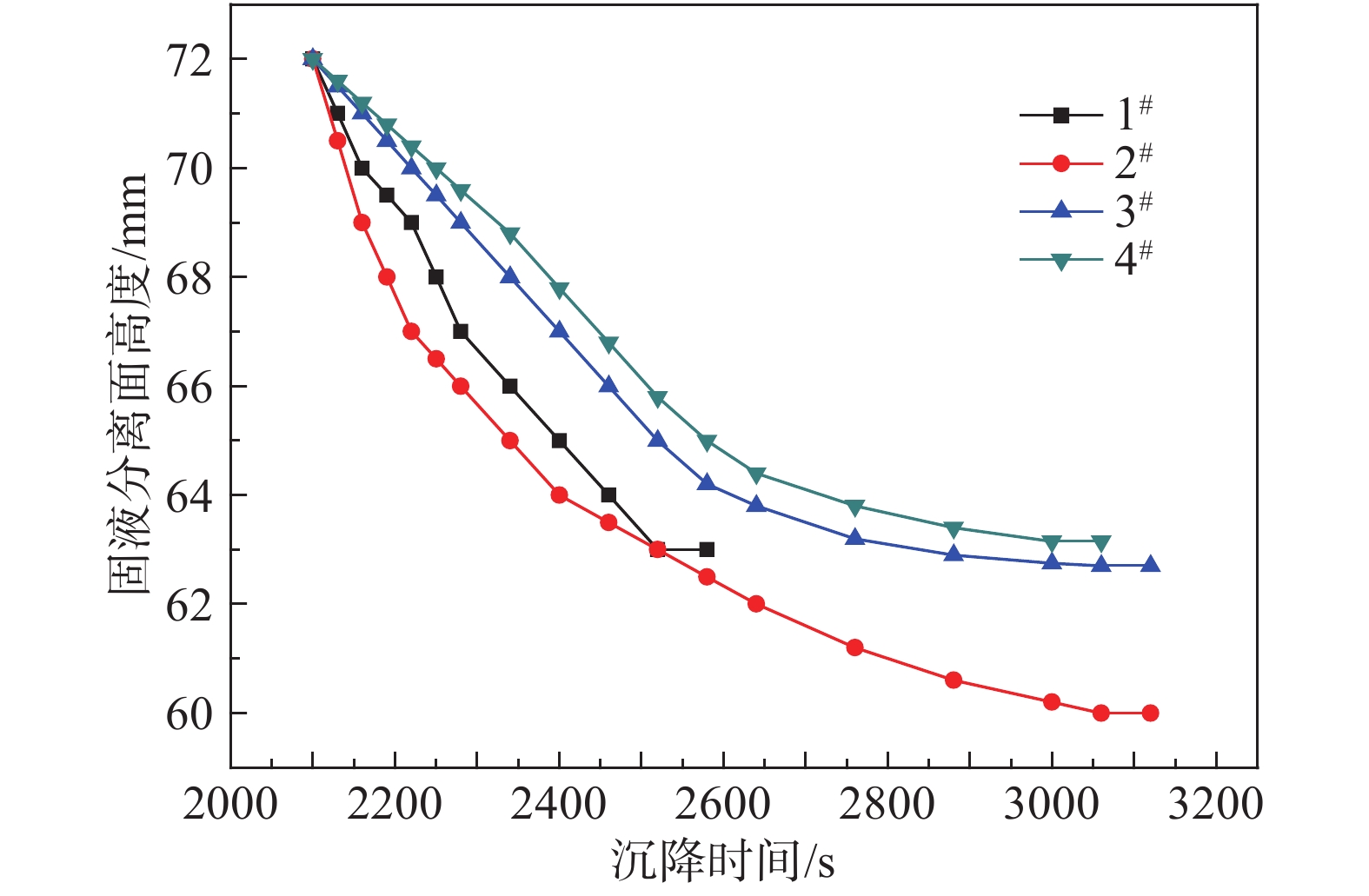
加入絮凝剂后,各组尾砂均从1000 mL(300 mm高度)降到240 mL刻度(72 mm高度)刻度后不再沉降,此时加入浓密增效剂,匀速搅拌后尾砂料浆继续沉降。选取效果较好的4组试验结果,分别记为1#、2#、3#、4#,加入浓密增效剂后各组尾砂从240 ml(72 mm高度)的刻度,降到最终刻度过程中固液分离面高度随时间变化的曲线如图4所示。由图4可以看出,加入浓密增效剂后,固液分离面高度继续下降,最大下降幅度为12 mm。沉降时间增加8~17 min。
只加絮凝剂的尾砂沉降的最终固相质量分数为72.29%,屈服应力为46.21 Pa,塑性黏度为0.23 Pa·s.加入絮凝剂各组别的最终固相质量分数与屈服应力如图5所示,与只加絮凝剂的尾砂料浆对比,添加多组分浓密增效剂后尾砂料浆最终固相质量分数增加了8.57%~10.13%,屈服应力降低了6.68~12.85 Pa,塑性黏度分别为0.54、0.51、0.38和1.12 Pa·s,变化较小。说明多组分浓密增效剂与单组分浓密增效剂相比不仅能降低单耗与成本,而且还能够发挥更大的作用,对尾砂浓密与管道输送起到较好的效果。
2.3 膏体充填材料抗压强度与成本分析
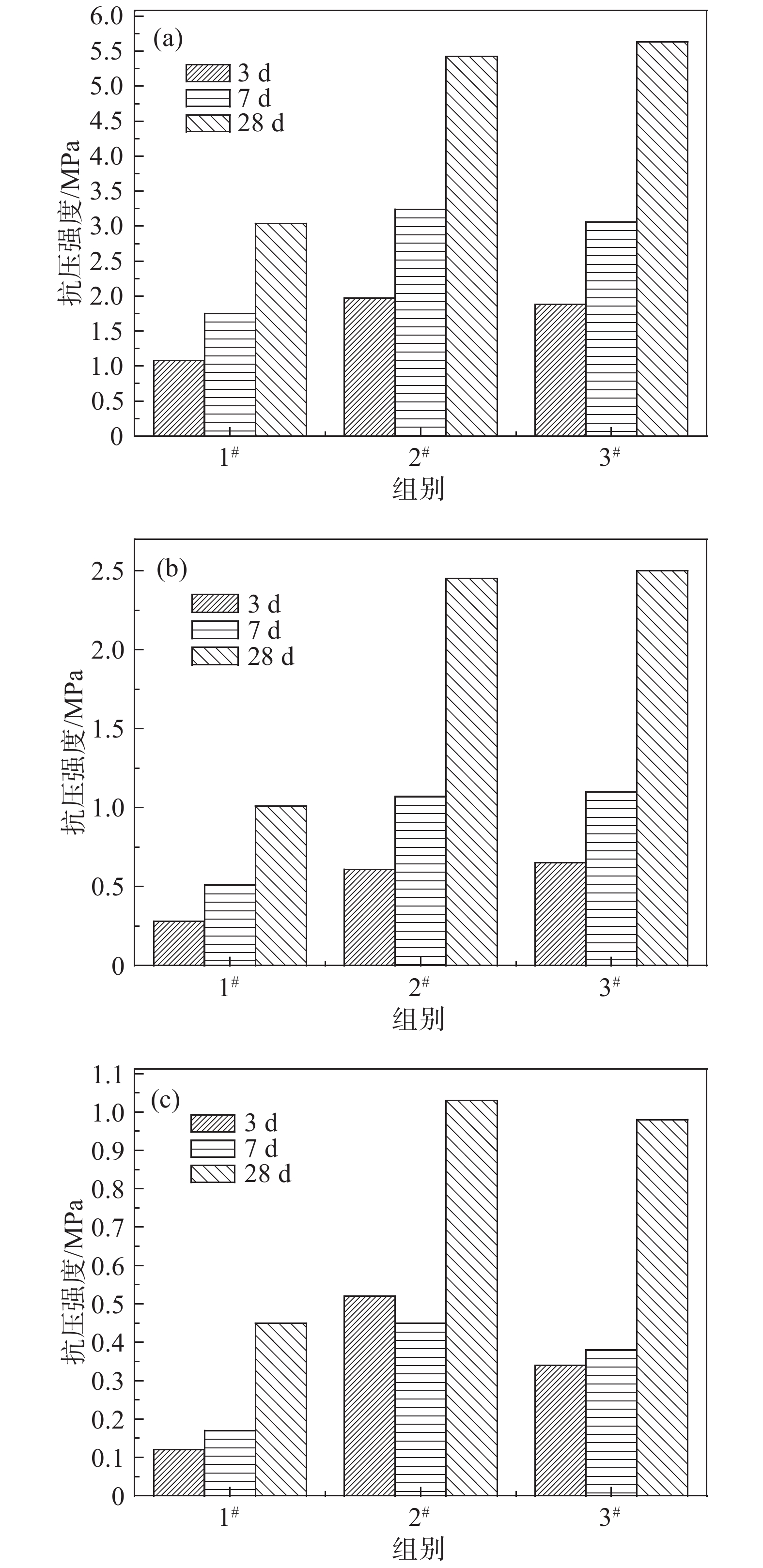
选出两组不同配比效果较好的浓密增效剂,分别为浓密增效剂Ⅰ与浓密增效剂Ⅱ。将浓密后的尾砂料浆与水泥(P.O 42.5)制成膏体充填材料,灰砂质量比分别为1∶6、1∶12与1∶24,对比添加浓密增效剂前后膏体充填材料的3、7与28 d抗压强度变化,如图6所示,其中1#为只加絮凝剂,浆体固相质量分数为72%;2#与3#分别为加入浓密增效剂Ⅰ与浓密增效剂Ⅱ,2#与3#浆体固相质量分数均为79%。
由图6可以看出,浓密增效剂添加后,由于料浆浓度的提高,相同灰砂质量比的膏体充填材料抗压强度显著提高;灰砂质量比1∶12并添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料28 d抗压强度与灰砂质量比1∶6未添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料强度的差值在20%以内。因此在满足强度要求的前提下可以降低灰砂比,即用灰砂比1∶12并添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料替代灰砂比1∶6未添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料;用灰砂比1∶24并添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料替代灰砂比1∶12未添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料,减少水泥用量,进而节约成本。对添加浓密增效剂前后进行成本分析,见表2。由表2可知,虽然灰砂比1∶12并添加浓密增效剂的膏体抗压强度相比灰砂比1∶6未添加浓密增效剂的膏体降低了将近20%,但是成本减少了40%;灰砂比1∶24并添加浓密增效剂的膏体抗压强度与灰砂比1∶12未添加浓密增效剂的膏体抗压强度相当,并且成本节约了30%。
表 2 成本分析Table 2. Cost analysis result浓密增效剂 灰砂质量比 28 d抗压强度/MPa 浓密增效剂成本/(元·t−1) 浓密增效剂、水泥、运输等总成本/(元·t−1) 节约成本/(元·t−1) 无 1∶6 3.04 0 125 0 Ⅰ 1∶12 2.45 8.5 75 50 Ⅱ 1∶12 2.50 6.5 72 53 无 1∶12 1.01 0 62.5 0 Ⅰ 1∶24 1.03 8.5 44 18.5 Ⅱ 1∶24 0.98 6.5 41 21.5 3. 浓密增效剂作用机理分析
3.1 碳吸附与电位试验分析
选取最佳配比的浓密增效剂,采用TOC吸附试验分析其吸附作用。配制A、B两种膏体与C、D两种溶液进行对比。A、B两种膏体由尾砂与水制成的固相质量分数为72%的浆体和絮凝剂或/和浓密增效剂组成的添加剂构成;C、D两种溶液由适量水和添加剂构成。添加剂具体组成如表3所示。通过TOC试验得出4种浆体与溶液的碳吸附结果见表4。其中A与C的差值m为尾砂料浆对絮凝剂中碳的吸附量,B与D的差值n为尾砂对絮凝剂与浓密增效剂的碳总吸附量,则m与n的差值r即为尾砂料浆对浓密增效剂的吸附量。由表4可以看出,浓密增效剂加入后,被尾砂所吸附,并使尾砂颗粒分散,释放出絮团中包裹的水。
表 3 添加剂的组成Table 3. Composition of additive试样 絮凝剂 浓密增效剂 质量分数/% 占试样质量分数/% 质量分数/% 占试样质量分数/% A 1 0.2 — — B 1 0.2 10 0.6 C 1 0.2 — — D 1 0.2 10 0.6 表 4 碳吸附试验结果Table 4. Carbon adsorption test resultsmg·g−1 A B C D m n r 70.36 70.56 81.09 93.26 10.73 22.7 11.97 选取最佳配比的浓密增效剂,采用Zeta电位试验分析其吸附作用。采用上述A与B两种浆体进行对比试验。通过电位试验得出两种浆体的试验结果分别为−0.7301与−1.7288 mV,添加了浓密增效剂的浆体其电位绝对值高于只加絮凝剂的浆体,说明浓密增效剂会吸附于尾砂颗粒表面使颗粒带电,颗粒间由于带相同电荷而相互排斥、加速颗粒间的分散。即浓密增效剂通过一定的静电斥力作用使得尾砂颗粒分散,从而打开絮凝结构,释放絮团间自由水。
3.2 浓密机理分析
浓密增效剂各组分的比重从大到小依次为水溶性高分子聚合物组分、络合组分与胺类组分,各组分通过不同的吸附与分散机理共同作用于絮团颗粒,改善浓密效果。
浓密增效剂的主要组分水溶性高分子聚合物之一是通过选择带有羧酸基、羟基、醚基、磺酸基等极性基的多种不饱和单体,在引发剂的作用下产生接枝共聚反应,形成具有梳型枝链结构的高分子共聚物。这种共聚物的主链与尾砂颗粒表面相连,而枝链延伸进入液相形成较厚的聚合物分子吸附层,当尾砂颗粒靠近,吸附层开始重叠,颗粒之间产生斥力作用,这种机械分离作用力即为空间位阻斥力作用。因此这种组分主要通过空间位阻斥力发挥作用,其分散作用机理如图7所示。
浓密增效剂的另一水溶性高分子聚合物组分为线性离子聚合物,由于亲水极性基团的电离作用,其静电斥力作用较强。浓密增效剂的络合组分含有羧酸基、羟基等可与水形成氢键的极性基团,具有较强的亲水作用,因此吸附在尾砂颗粒表面后会形成一层水化膜,水化膜会破坏絮团结构,释放絮团间的自由水,使颗粒表面更加湿润,起到润滑作用,从而改善尾砂浓密后的流动性。浓密增效剂的胺类组分具有一定的引气作用,能够降低液气界面张力,因此可以吸附在液气界面上形成水化膜,同样起到润滑作用,改善流动性。故浓密增效剂的分散作用是通过各组分的空间位阻斥力作用、静电斥力作用和水化膜润滑作用共同实现的。
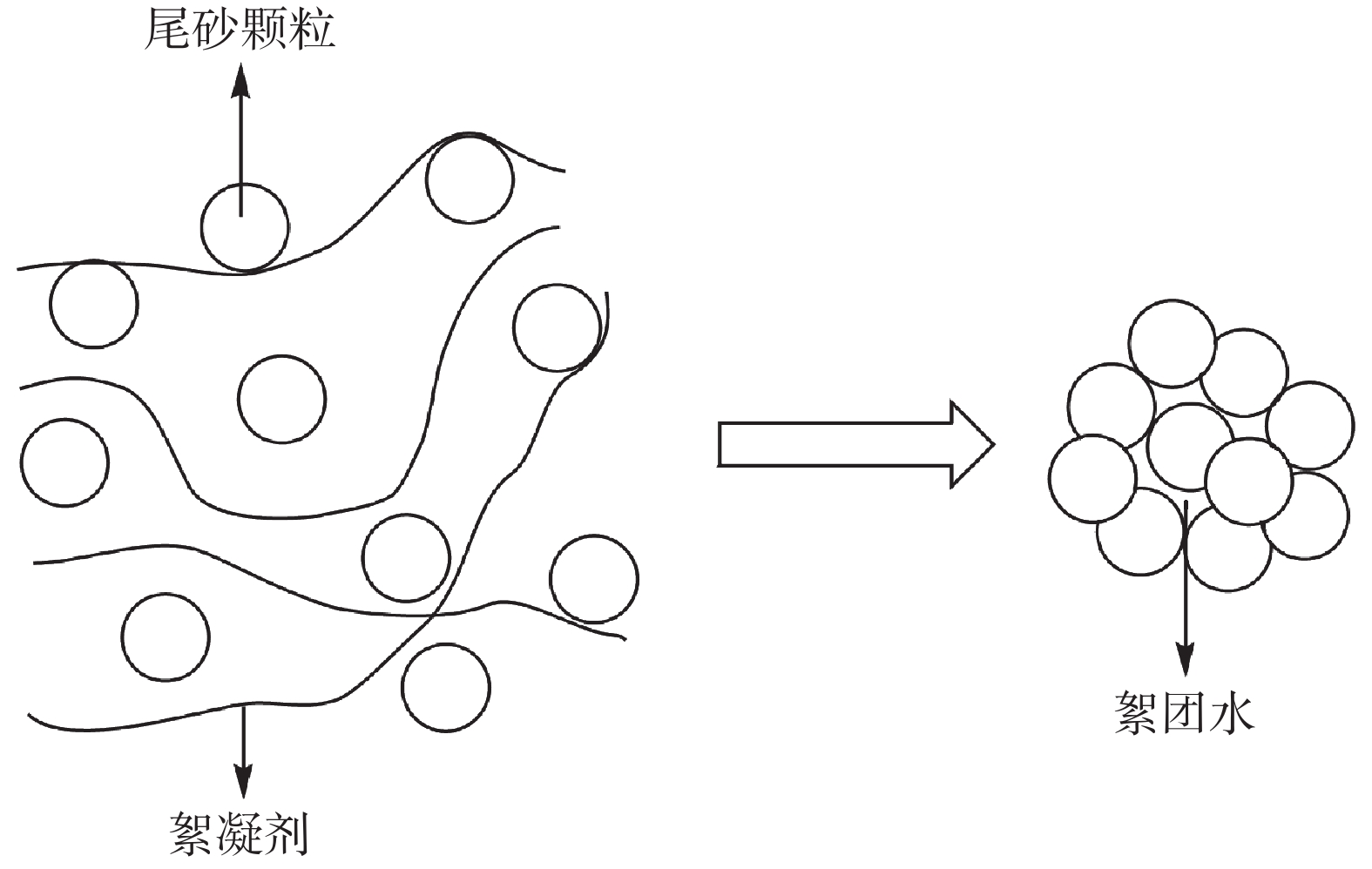
絮凝剂为高分子长链状结构,高分子链会网捕尾砂颗粒,进行“架桥作用”,随着网捕颗粒数量的增加,逐渐形成絮团,其作用机理示意图如图8所示。将一定浓度的絮凝剂溶液加入浓密机中与低浓度的尾砂料浆充分混合后,絮凝剂会使尾砂料浆中的微细颗粒凝聚、吸附成团,形成紧密接触的大颗粒絮团,靠自重而迅速沉降直至浓密机底部,因此沉降速度提高。
沉降至浓密机底部的尾砂颗粒之间存在着絮团水,待尾砂沉降完毕后,在浓密机底部泥层添加一定浓度的浓密增效剂溶液并搅拌,使浓密增效剂均匀的混合在泥层中与絮团颗粒充分结合。浓密增效剂通过吸附和分散,会打开絮凝结构,降低颗粒固液界面能,释放絮团间的自由水,水通过导水杆被排出,从而可以进一步提高尾砂浓密后的浓度。通过浓密增效剂的作用可将底流固相质量分数较未添加浓密增效剂时提高8.57%~10.13%,同时,能够降低屈服应力,改善尾砂颗粒的流动性。并且制成膏体后,浓密增效剂的分散作用又会使水泥水化程度提高,进而可以提高膏体充填材料的抗压强度。
4. 结论
(1)通过单组分浓密增效剂试验发现,加入絮凝剂沉降完毕后再加入浓密增效剂的浓度显著提高且沉降时间增加较少,效果好,可以确定其为最佳添加工艺。并且浓密增效剂可以改善尾砂浓密后的流变性能,料浆固相质量分数可提高8.57%~10.13%,同时屈服应力降低6.68~12.85 Pa,从而有利于管道输送。
(2)多组分浓密增效剂与单组分浓密增效剂相比不仅能降低单耗与成本,而且还能够发挥更大的作用,多组分浓密增效剂可以提高膏体充填材料的抗压强度,即灰砂质量比1∶12并添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料28 d抗压强度为2.5 MPa,与灰砂质量比1∶6未添加浓密增效剂的膏体充填材料强度相差小于20%。
(3)通过碳吸附与电位试验发现,浓密增效剂具有吸附与分散的作用,会打开絮凝结构,降低颗粒固液界面能,并释放絮团水,从而提高尾砂浓度,并改善尾砂颗粒的流动性。浓密增效剂的分散作用是通过各组分的空间位阻斥力作用、静电斥力作用和水化膜润滑作用共同实现的。
-
表 1 尾砂的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of tailings
% SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 K2O MgO CaO MnO Na2O TiO2 SO3 P2O5 65.83 16.89 2.30 7.46 0.31 3.46 0.08 1.53 0.29 0.60 0.09 表 2 成本分析
Table 2 Cost analysis result
浓密增效剂 灰砂质量比 28 d抗压强度/MPa 浓密增效剂成本/(元·t−1) 浓密增效剂、水泥、运输等总成本/(元·t−1) 节约成本/(元·t−1) 无 1∶6 3.04 0 125 0 Ⅰ 1∶12 2.45 8.5 75 50 Ⅱ 1∶12 2.50 6.5 72 53 无 1∶12 1.01 0 62.5 0 Ⅰ 1∶24 1.03 8.5 44 18.5 Ⅱ 1∶24 0.98 6.5 41 21.5 表 3 添加剂的组成
Table 3 Composition of additive
试样 絮凝剂 浓密增效剂 质量分数/% 占试样质量分数/% 质量分数/% 占试样质量分数/% A 1 0.2 — — B 1 0.2 10 0.6 C 1 0.2 — — D 1 0.2 10 0.6 表 4 碳吸附试验结果
Table 4 Carbon adsorption test results
mg·g−1 A B C D m n r 70.36 70.56 81.09 93.26 10.73 22.7 11.97 -
[1] 吴爱祥, 杨莹, 程海勇, 等. 中国膏体技术发展现状与趋势. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(5):517 Wu A X, Yang Y, Cheng H Y, et al. Status and prospects of paste technology in China. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(5): 517
[2] 缪协兴, 钱鸣高. 中国煤炭资源绿色开采研究现状与展望. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2009, 26(1):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2009.01.001 Miao X X, Qian M G. Research on green mining of coal resources in China: current status and future prospects. J Min Saf Eng, 2009, 26(1): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2009.01.001
[3] 王丽红, 鲍爱华, 罗园园. 中国充填技术应用与展望. 矿业研究与开发, 2017, 37(3):1 Wang L H, Bao A H, Luo Y Y. Development and outlook on the filling method in China. Min Res Dev, 2017, 37(3): 1
[4] 常庆粮, 周华强, 柏建彪, 等. 膏体充填开采覆岩稳定性研究与实践. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2011, 28(2):279 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2011.02.021 Chang Q L, Zhou H Q, Bai J B, et al. Stability study and practice of overlying strata with paste backfilling. J Min Saf Eng, 2011, 28(2): 279 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3363.2011.02.021
[5] 吴爱祥, 王勇, 王洪江. 膏体充填技术现状及趋势. 金属矿山, 2016(7):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.07.001 Wu A X, Wang Y, Wang H J. Status and prospects of the paste backfill technology. Metal Mine, 2016(7): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2016.07.001
[6] 刘琼, 张希巍. 中国膏体充填技术研究进展概述. 现代矿业, 2016(5):1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2016.05.001 Liu Q, Zhang X W. Overview of the research progress of the paste backfill technology in China. Mod Min, 2016(5): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6082.2016.05.001
[7] 李公成, 王洪江, 吴爱祥, 等. 基于动态沉降压密实验的深锥浓密机关键参数确定. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(8):1693 Li G C, Wang H J, Wu A X, et al. Key parameters determination of deep cone thickener based on dynamical settling and compaction experiments. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2017, 27(8): 1693
[8] 吴爱祥, 杨莹, 王贻明, 等. 深锥浓密机底流浓度模型及动态压密机理分析. 工程科学学报, 2018, 40(2):152 Wu A X, Yang Y, Wang Y M, et al. Mathematical modelling of underflow concentration in a deep cone thickener and analysis of the dynamic compaction mechanism. Chin J Eng, 2018, 40(2): 152
[9] 王洪江, 王勇, 吴爱祥, 等. 细粒全尾动态压密与静态压密机理. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(5):566 Wang H J, Wang Y, Wu A X, et al. Dynamic compaction and static compaction mechanism of fine unclassified tailings. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(5): 566
[10] 吴爱祥, 周靓, 尹升华, 等. 全尾砂絮凝沉降的影响因素. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(2):439 Wu A X, Zhou J, Yin S H, et al. Influence factors on flocculation sedimentation of unclassified tailings. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2016, 26(2): 439
[11] 焦华喆, 王洪江, 吴爱祥, 等. 全尾砂絮凝沉降规律及其机理. 北京科技大学学报, 2010, 32(6):702 Jiao H Z, Wang H J, Wu A X, et al. Rule and mechanism of flocculation sedimentation of unclassified tailings. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2010, 32(6): 702
[12] 李辉, 王洪江, 吴爱祥, 等. 基于尾砂沉降与流变特性的深锥浓密机压耙分析. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(12):1553 Li H, Wang H J, Wu A X, et al. Pressure rake analysis of deep cone thickeners based on tailings’ settlement and rheological characteristics. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(12): 1553
[13] 王勇, 吴爱祥, 王洪江, 等. 絮凝剂用量对尾矿浓密的影响机理. 北京科技大学学报, 2013, 35(11):1419 Wang Y, Wu A X, Wang H J, et al. Influence mechanism of flocculant dosage on tailings thickening. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2013, 35(11): 1419
[14] 王勇, 吴爱祥, 王洪江, 等. 絮凝和稀释对尾矿沉降性能的影响及工程建议. 武汉理工大学学报, 2014, 36(9):114 Wang Y, Wu A X, Wang H J, et al. Effect of flocculation and dilution on the tailings setting performance and project proposal. J Wuhan Univ Technol, 2014, 36(9): 114
[15] 杨柳华, 王洪江, 吴爱祥, 等. 絮凝沉降对全尾砂料浆流变特性的影响. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(10):3523 Yang L H, Wang H J, Wu A X, et al. Effect of flocculation settling on rheological characteristics of full tailing slurry. J Cent South Univ Sci Technol, 2016, 47(10): 3523
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 丁维波,王丹影,程磊,阮泽宇,贺军,王石. 含残留APAM全尾砂料浆管输过程粗颗粒尾砂垂向分布特征. 洁净煤技术. 2024(S1): 650-658 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王洪江,王小林,张玺,吴爱祥,田志刚,杜向红. 超细全尾砂深锥动态絮凝浓密试验. 工程科学学报. 2022(02): 163-169 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 阮竹恩,吴爱祥,焦华喆,李翠平,李公成,莫逸,王洪江. 我国全尾砂料浆浓密研究进展与发展趋势. 中国有色金属学报. 2022(01): 286-301 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘娟红,周在波. 细粒级金属尾砂的综合利用及在矿山充填中存在的问题和对策. 金属矿山. 2022(07): 240-249 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 陈格仲,李翠平,阮竹恩,侯贺子. 膏体充填中絮凝条件对絮团结构及固液分离效率的影响. 中国有色金属学报. 2022(10): 3169-3182 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李翠平,陈格仲,侯贺子,颜丙恒. 面向膏体充填尾砂浓密的絮团结构研究进展综述. 金属矿山. 2021(01): 14-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. Di Zheng,Wei-dong Song,Yu-ye Tan,Shuai Cao,Zi-long Yang,Li-juan Sun. Fractal and microscopic quantitative characterization of unclassified tailings flocs. International Journal of Minerals Metallurgy and Materials. 2021(09): 1429-1439 .  必应学术
必应学术
8. 任建平,焦华喆. 全尾砂半工业环管输送试验与数值模拟研究. 矿业研究与开发. 2020(12): 23-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: